In Canada, creditors such as banks, credit card, and loan companies report to two major credit agencies, Equifax and TransUnion.
From this combined report you are given a credit score from 300 – 900, and this score represents your creditworthiness when you apply for credit.
Ideally, you want a score above 680 to qualify for credit and receive favorable rates.
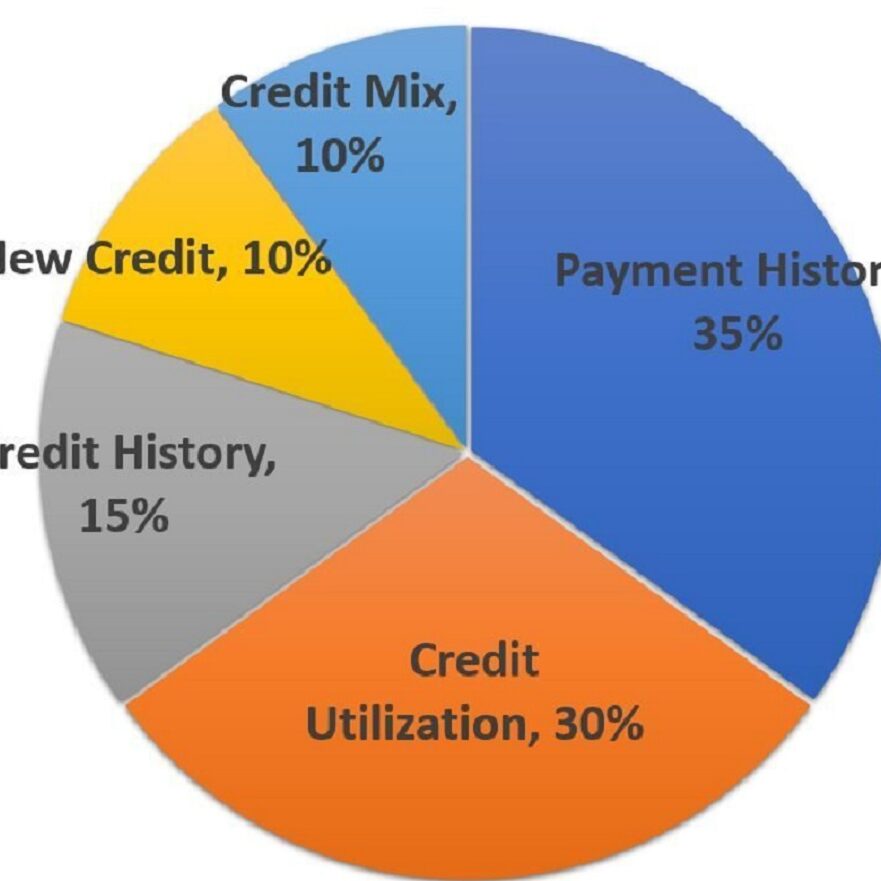
These are the 5 main variables that factor into your credit score and how they are weighted:
1. Payment History (35%)
How timely you pay your bills is the biggest factor that affects your credit score. The number of late payments on your credit facilities is all recorded on your credit report. Make sure you pay at least your minimum monthly payments.
2. Utilization (30%)
Utilization is how much your credit balance is relative to your credit limit. For example, if you have a $1000.00 credit card and you owe $900.00, you are at 90% utilization. This high utilization would have a negative effect on your credit. Ideally, you want to be below 50%. If you have other credit facilities, you would be better off spreading the balance between them.
3. History (15%) –
It helps your credit score to have more established credit facilities. Having ‘older’ accounts is better for your score. Therefore it is not advisable for you to keep opening and closing accounts.
4. New Credit (10%)
Applying for credit can have a negative impact on your score if you do it too often. This can be looked upon as you are a ‘credit seeker’. Please note there is a difference between a ‘soft’ and a ‘hard’ inquiry. Inquiries that do not lead to credit being extended are ‘soft’ inquiries and do not affect your credit score. An example of this would be your utility company obtaining a credit score to open a new account. ‘Hard’ inquiry examples are credit, loan, and mortgage applications.
5. Credit Mix (10%)
Having different types of credit facilities help build your credit score, as it demonstrates how you handle different types of credit.
Two main types of credit accounts:
i) Revolving – Minimum payment is based on the balance and as you pay down the balance, the credit becomes available for you to use again.
ie. credit cards and lines of credit
ii) Installment – There is a fixed payment and when you pay down the balance you cannot use the credit again.
ie. Car loans and student loans
These are the main variables that influence your credit score. Employment status, income, bank account balances, and your overall net worth may affect your credit approval but they do not directly affect your score.